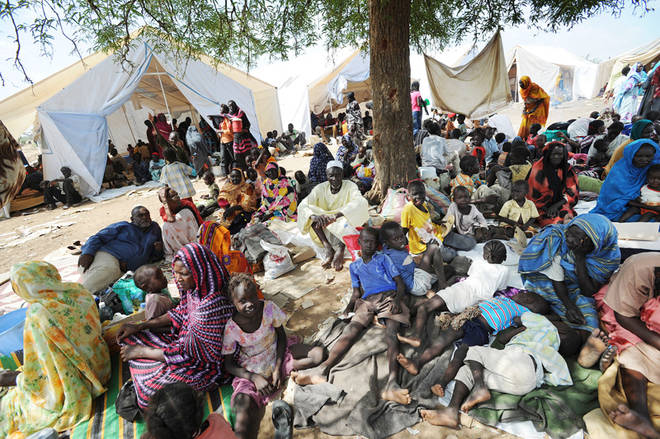
No fewer than 71 million people have been displaced worldwide from war, persecution and other violence, the U.N. refugee agency said Wednesday.
According to the record, this is an increase of more than 2 million from last year and an overall total that will amount to the world’s 20th most populous country.
The annual “Global Trends” report released by the U.N. High Commissioner for Refugees counts the number of the world’s refugees, asylum-seekers and internally displaced people at the end of 2018, in some cases following decades of living away from home.
The figures, coming on the eve of World Refugee Day on Thursday, are bound to add fuel to a debate at the intersection of international law, human rights and domestic politics, especially the movement in some countries, including the U.S., against immigrants and refugees.
Launching the report, the high commissioner, Filippo Grandi, had a message for U.S. President Donald Trump and other world leaders, calling it “damaging” to depict migrants and refugees as threats to jobs and security in host countries. Often, they are fleeing insecurity and danger themselves, he said.
The report also puts a statistical skeleton onto often-poignant individual stories of people struggling to survive by crossing rivers, deserts, seas, fences and other barriers, natural and man-made, to escape government oppression, gang killings, sexual abuse, militia murders and other such violence at home.
UNHCR said 70.8 million people were forcibly displaced at the end of last year, up from about 68.5 million in 2017 — and nearly a 65% increase from a decade ago. Among them, nearly three in five people — or more than 41 million people — have been displaced within their home countries.
“The global trends, once again unfortunately, go in what I would say is the wrong direction,” Grandi told reporters in Geneva. “There are new conflicts, new situations, producing refugees, adding themselves to the old ones. The old ones never get resolved.”
The phenomenon is both growing in size and duration. Some four-fifths of the “displacement situations” have lasted more than five years. After eight years of war in Syria, for instance, its people continue to make up the largest population of forcibly displaced people, at some 13 million.
Amid runaway inflation and political turmoil at home, Venezuelans for the first time accounted for the largest number of new asylum-seekers in 2018, with more than 340,000 — or more than one in five worldwide last year. Asylum-seekers receive international protection as they await acceptance or rejection of their requests for refugee status.
UNHCR said that its figures are “conservative” and that Venezuela masks a potentially longer-term trend.
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days ago
 Entertainment7 days ago
Entertainment7 days ago
 Crime6 days ago
Crime6 days ago
 Education1 week ago
Education1 week ago
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week ago
 Comments and Issues6 days ago
Comments and Issues6 days ago
 Football7 days ago
Football7 days ago
 Latest6 days ago
Latest6 days ago

