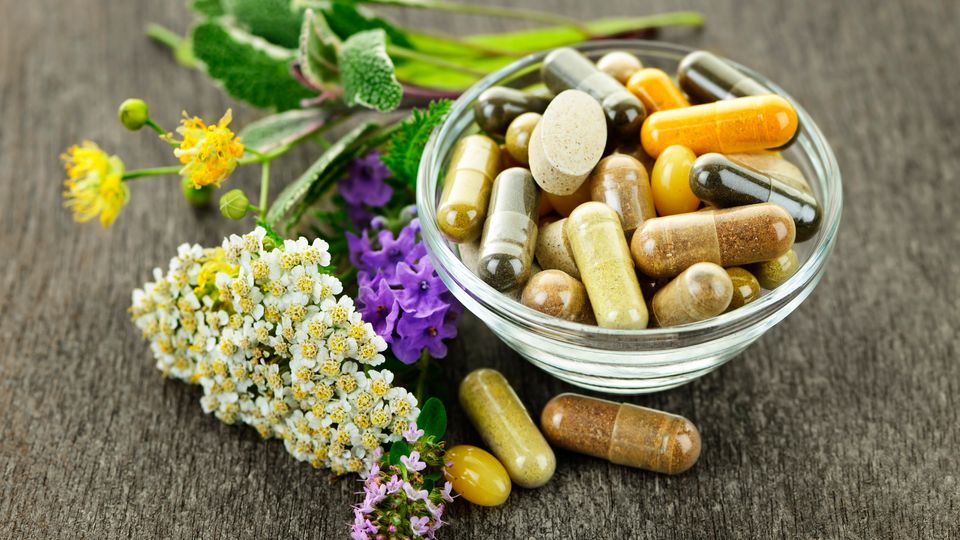
Herbal supplements have surged in popularity, especially through promotions on platforms like TikTok.
However, new research from the University of Michigan reveals that several widely-used supplements could pose serious risks to your liver.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, analyzed data from more than 9,500 American adults, focusing on six herbal supplements previously linked to liver toxicity: ashwagandha, black cohosh, garcinia cambogia, green tea extract, red yeast rice, and turmeric
Researchers found that nearly 58 percent of participants reported using an herbal or dietary supplement in the past 30 days, with about five percent consuming at least one of the potentially harmful supplements.
Extrapolating these findings, researchers estimate that 15.6 million adults in the U.S. could be using supplements that may damage their liver.
“Given a lack of regulatory oversight on the manufacturing and testing of botanical products, clinicians should be aware of possible adverse events from consumption of these largely unregulated products,” the study authors noted.
The supplement industry is largely unregulated, which raises concerns about product safety.
READ ALSO: Artificial sweeteners linked to liver damage, studies show
“What the label says may not be what’s actually in the bottle,” warns Jessica Cording, MS, RD, author of The Little Book of Game-Changers: 50 Healthy Habits For Managing Stress & Anxiety. Although the study did not confirm that the supplements cause liver damage, it highlighted the potential risks associated with their use.
Kelly Johnson-Arbor, MD, a toxicologist at MedStar Health, stresses the importance of caution. “Just because these products are sold as ‘over-the-counter’ supplements and do not require a prescription, does not necessarily mean that they are safe,” she says.
Experts recommend consulting a licensed healthcare provider before starting any herbal supplement regimen.
“Herbal supplements can be powerful, and just because it’s an herb doesn’t mean it’s risk-free,” Cording advises. Given the potential for interactions with other medications and the risk of overuse, professional guidance is crucial to ensure safety.
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week ago
 News1 week ago
News1 week ago
 Trends2 days ago
Trends2 days ago
 Latest1 day ago
Latest1 day ago
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week ago
 Business1 week ago
Business1 week ago
 Crime1 week ago
Crime1 week ago
 Crime1 week ago
Crime1 week ago

