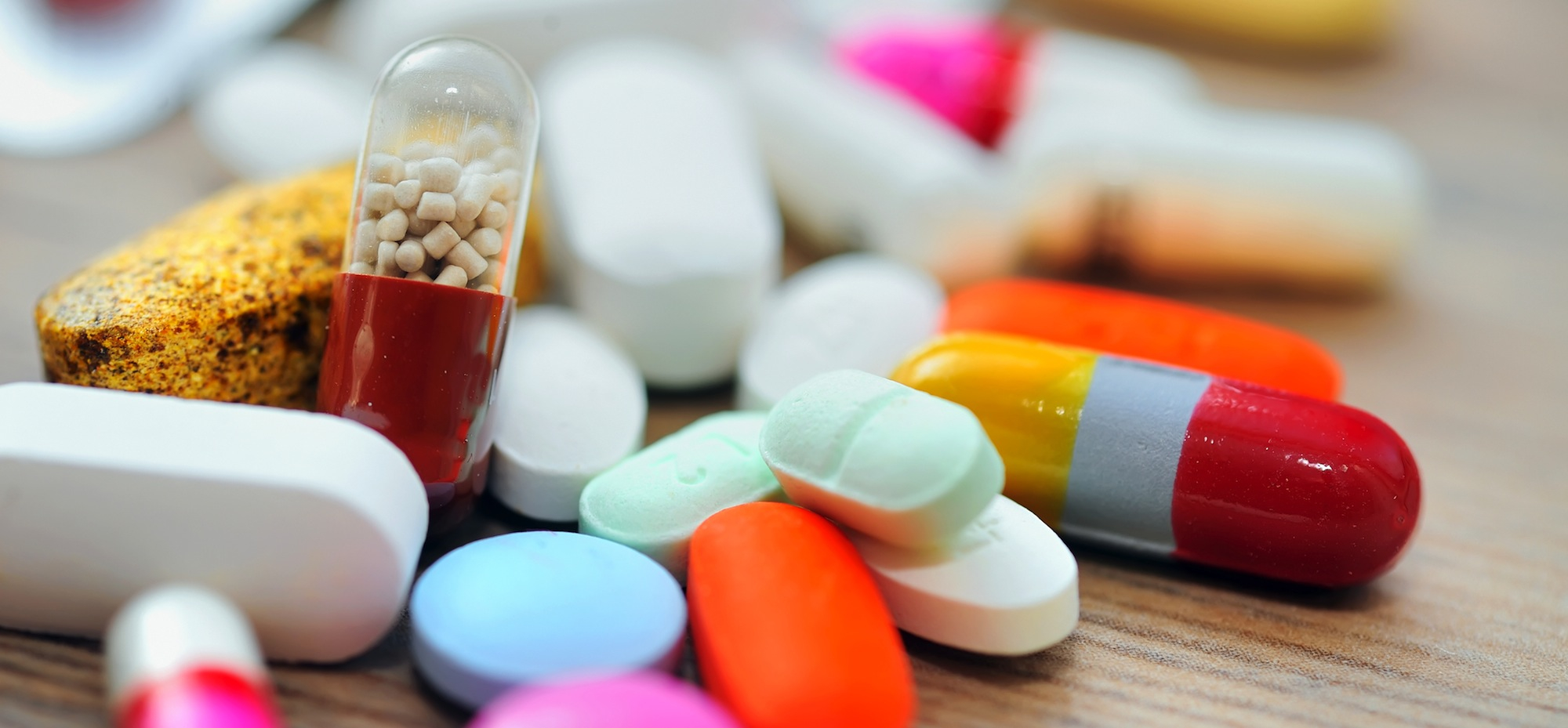
A recent study conducted by the European Sudden Cardiac Arrest network has unveiled a potential association between a widely prescribed medication for high blood pressure and an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
This research has prompted a call for caution among both doctors and patients when considering the use of this medication for managing blood pressure.
Understanding Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Sudden cardiac arrest is a critical medical event characterized by the abrupt cessation of the heart’s beating, resulting in the loss of blood flow to the body.
It accounts for approximately half of all cardiac-related deaths in Europe and contributes to one in five natural fatalities.
Symptoms of sudden cardiac arrest include irregular breathing patterns and loss of consciousness, and without prompt intervention, it can swiftly lead to fatality.
Investigating the Medication’s Link to Sudden Cardiac Arrest
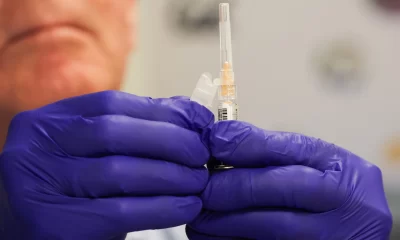
This study focused on two commonly prescribed medications: nifedipine and amlodipine, both employed to treat high blood pressure and chest pain.
Researchers meticulously examined data from thousands of patients and healthy individuals to ascertain whether a correlation existed between these medications and sudden cardiac arrest.
The research outcomes revealed a notable connection between high doses of nifedipine and an elevated risk of sudden cardiac arrest. In contrast, no such association was observed with amlodipine.
Surprising Findings and the Need for Further Research
The findings took researchers by surprise, given that both nifedipine and amlodipine have been widely utilized for many years without any reported concerns.
Prior research had not identified this association, primarily due to the challenges associated with studying the rapid onset of sudden cardiac arrest.
ALSO READ: Signs of sudden cardiac arrest people above 35 and 45 should not ignore
The study underscores the necessity for additional research to validate these findings before any actions are taken by medical practitioners or patients.
Implications for Patients and Doctors
While further research is imperative, this study emphasizes the importance of prudence when prescribing high-dose nifedipine to individuals with high blood pressure.
Patients with hypertension are encouraged to maintain vigilance and closely monitor their symptoms while using this medication.
Should they experience symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea—potentially indicative of sudden cardiac arrest—they should promptly consult their healthcare providers.
For medical practitioners, it is crucial to exercise caution when prescribing high-dose nifedipine, especially to patients with underlying cardiac conditions.
Exploring alternative medications or adjusting the dosage of nifedipine may help mitigate the risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
The Importance of Continued Research
This study underscores the significance of ongoing research into the causes and treatments of sudden cardiac arrest.
Further investigations are essential to affirm the link between nifedipine and sudden cardiac arrest and to determine whether other commonly prescribed medications for high blood pressure and chest pain may also be associated with this condition.
In conclusion, while medications like nifedipine effectively manage high blood pressure and chest pain, their use warrants caution to avert potential risks and complications.
Patients must diligently monitor their symptoms, and healthcare providers should factor in potential risks when prescribing these medications.
Ongoing research will enhance our comprehension of sudden cardiac arrest and guide healthcare professionals in delivering the best possible care to patients.
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days ago
 Entertainment7 days ago
Entertainment7 days ago
 Crime5 days ago
Crime5 days ago
 Education7 days ago
Education7 days ago
 Health7 days ago
Health7 days ago
 Comments and Issues6 days ago
Comments and Issues6 days ago
 Football6 days ago
Football6 days ago
 Latest6 days ago
Latest6 days ago

