Boko Haram was first on the list of priorities at an international security summit held in the Nigerian capital Abuja on Saturday.
The Second Regional Security Summit, attended by French President François Hollande and British Foreign Secretary Philip Hammond, among others, came two years after the first conference was convened in Paris.
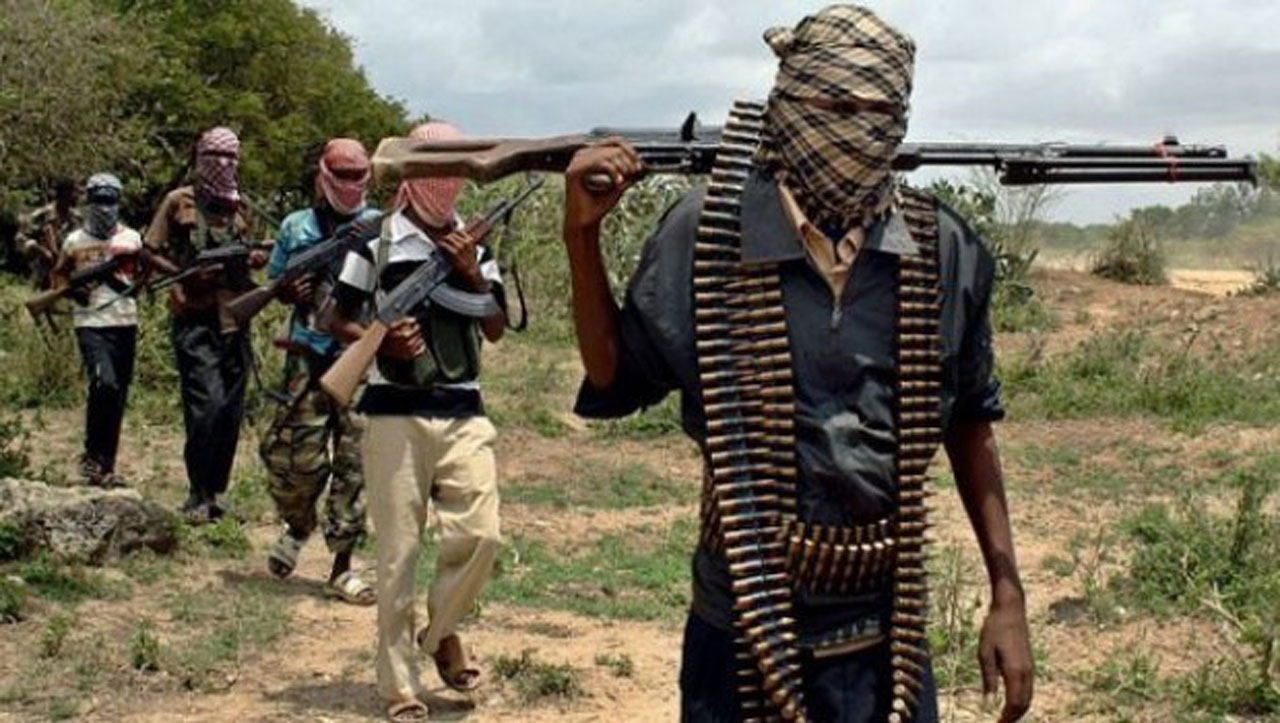
Since then, Nigeria and its neighbors have made progress in tackling the threat posed by Boko Haram. A Multi-National Joint Task Force (MNJTF)—consisting of troops from Nigeria, Cameroon, Chad, Niger and Benin—has been battling the group for more than a year and has reduced the territory it controls, despite the fact that Boko Haram continues to carry out suicide bombings on a sporadic basis.
Here are four key takeaways from the conference:
- Libya Is the Key to Severing the Boko Haram-ISIS Connection
Since March 2015, Boko Haram has rebranded itself as Islamic State West Africa Province (ISWAP) following a pledge of allegiance to the Islamic State militant group (ISIS). But despite this aesthetic change, it is difficult to gauge how much of an impact this affiliation has had on Boko Haram’s modus operandi, particularly with ISIS’s main hub being thousands of miles away in Syria and Iraq.
This could change if ISIS is able to increase its influence and reach in Libya. ISIS is believed to have thousands of fighters in the lawless North African state and controls the coastal city of Sirte. “If we see Daesh establish a stronger presence in Libya, that feels much more to people here [in Nigeria] like a direct communications route, that is likely to step up the practical collaboration between the two groups,” Hammond said at the conference.
- Europe Still Sees Boko Haram as a Threat
Since its inceptions, Boko Haram’s key objective—the establishment of an Islamic caliphate in northern Nigeria—has been largely domestic. In 2015, the group extended its attacks to other countries in the region, particularly those participating in the MNJTF. The fallout from the security summit makes clear, however, that European leaders remain worried about the group.
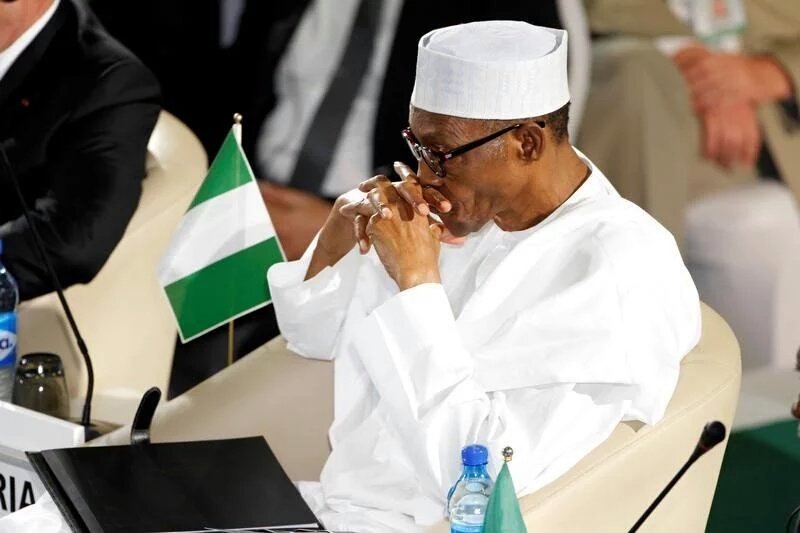
Hollande stated that, despite the “impressive” gains made against Boko Haram under the administration of Nigerian President Muhammadu Buhari, the group “remains a threat.” European Union High Representative Federica Mogherini also confirmed that 50 million euros ($56.6 million) had been set aside to assist the MNJTF in its mission.
ALSO SEE: Illegal arms: Ethnic militiamen stockpile arms
- Boko Haram Is Not Nigeria’s Only Problem
The Buhari administration’s success at tackling Boko Haram—the group has now been confined to the remote Sambisa Forest in the northeast Borno state after its territorial gains were rolled back—means that some of the other security threats it faces have come into sharper focus.
One particular issue rearing its head at present is the revival in militancy among groups in the Niger Delta. Nigeria’s oil output has been severely hit by attacks on pipelines, and a newly-formed group calling itself the Niger Delta Avengers recently shut down a facility run by U.S. company Chevron after an attack, cutting off 35,000 barrels per day. Shell has also evacuated staff from the Bonga oil field in the region as the threat of attack grows.
Hammond described the events in the Niger Delta as “a major concern” and said that simply relocating Nigerian military forces to the region wouldn’t deal with the root problems. “Buhari has got to show as a president from the north that he is not ignoring the Delta, that he is engaging with the challenges in the Delta,” said the British foreign secretary.
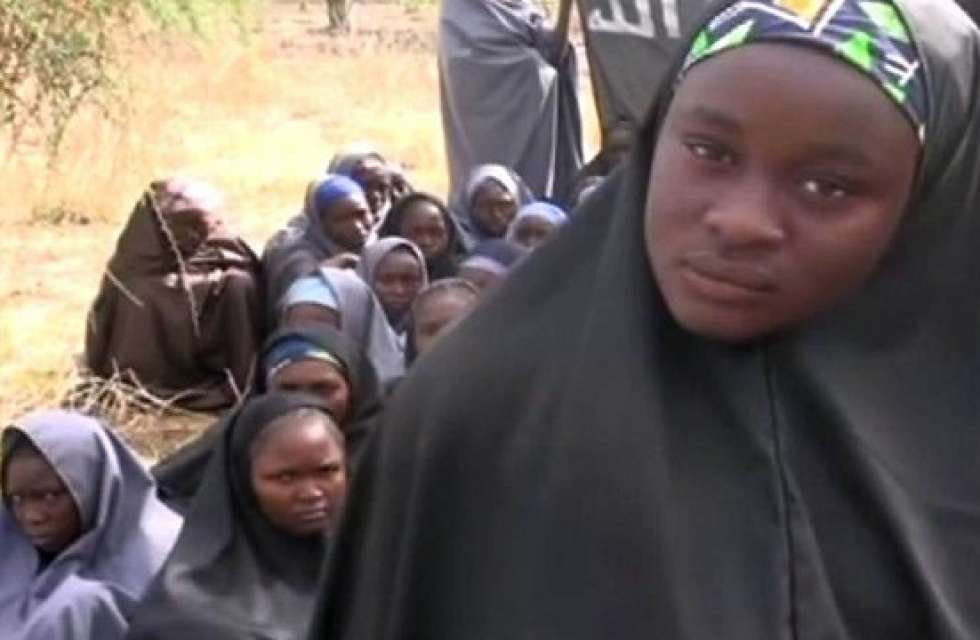
- The Chibok Girls Continue to Haunt Nigeria
Upon his presidential inauguration in May 2015, Buhari said that Nigeria would not have defeated Boko Haram until all abductees—including the Chibok girls—were rescued from the group. It has been more than two years since Boko Haram militants abducted 276 girls from their school in Chibok, Borno state, and 219 remain missing. Despite recent glimmers of hope—such as a proof-of-life video released in April in which several of the girls were identified—it is not clear that Nigeria is any closer to rescuing the girls.
Buhari stressed in his speech to the summit that Nigeria has a “firm commitment to safely rescue and reunite the abducted Chibok girls, and indeed all other abductees with their families.” But in December 2015, the Nigerian president admitted that he had “no firm intelligence” on their whereabouts.
Source; Newsweek
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week ago
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week ago
 Latest6 days ago
Latest6 days ago
 News7 days ago
News7 days ago
 Business5 days ago
Business5 days ago
 Business1 week ago
Business1 week ago
 Football1 week ago
Football1 week ago
 Business1 week ago
Business1 week ago








