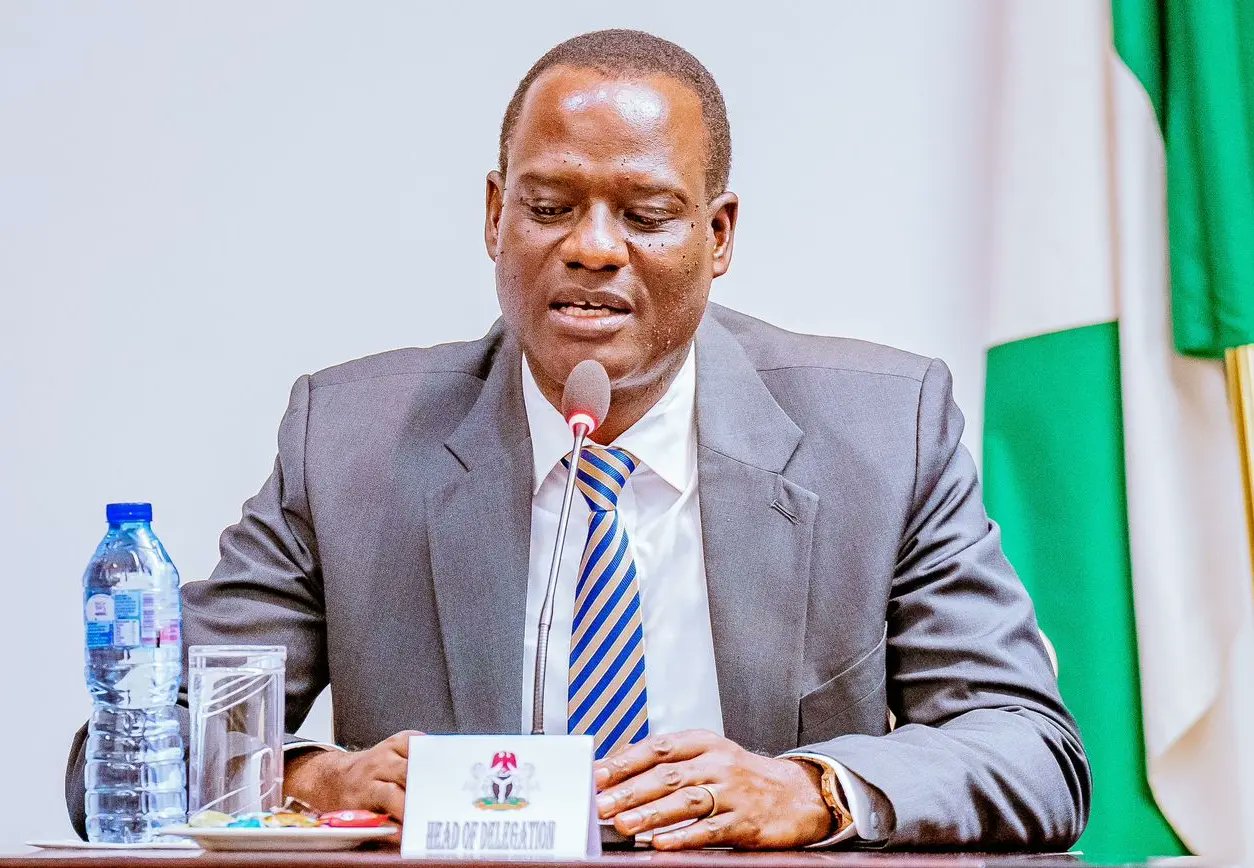
The newly proposed Economic Stabilisation Bills (ESBs) in Nigeria, recently approved by the Federal Executive Council (FEC), mark a significant step towards addressing the nation’s fiscal and economic challenges.
Taiwo Oyedele, chairman of the presidential fiscal policy and tax reforms committee, outlined the key aspects of these bills, which are part of the government’s Accelerated Stability and Advancement Plan (ASAP).
The ESBs seek to amend 15 tax and fiscal laws, aiming for economic stability and sustained inclusive growth.
Key Focus Areas
Inflation Control and Monetary Support:
A core focus of the ESBs is to complement monetary policies aimed at reducing inflation, stabilizing prices, and strengthening the naira.
The bills propose reforms to Nigeria’s foreign exchange (forex) regime, enhancing the Central Bank of Nigeria’s regulatory powers and promoting exchange rate convergence.
Employment and Export Promotion:
Several of the proposed amendments target job creation and export diversification. Income tax laws would be adjusted to encourage domestic employment, particularly within the digital economy.
The bills also propose tax incentives for private sector employers offering wage awards and transport subsidies, as well as relief for companies generating incremental employment.
Support for the Gas Sector and Small Businesses:
Another significant area of reform is the gas industry, where the bills seek to simplify local content requirements, ensuring global competitiveness.
Moreover, collaboration with state governments to suspend certain taxes and levies on small businesses and vulnerable populations aims to ease the financial burden on these groups.
Implications for Nigeria’s Economic Growth
The ESBs are designed to stabilize Nigeria’s economy amidst mounting fiscal and structural challenges.
By focusing on tax reliefs, job creation, and easing small business operations, the government aims to stimulate domestic economic activity while maintaining fiscal discipline.
The proposals also aim to widen the tax net through the Tax Identification Consolidation and Collaboration (TICC) initiative, fostering a more inclusive and fairer tax environment.
While these reforms hold promise, the real test will come as the bills are debated and, potentially, passed into law by the National Assembly.
Their effectiveness will largely depend on implementation and the ability to balance fiscal consolidation with the needs of businesses and households struggling with rising costs and currency volatility.
 Entertainment5 days ago
Entertainment5 days ago
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week ago
 Health4 days ago
Health4 days ago
 Football1 week ago
Football1 week ago
 Football1 week ago
Football1 week ago
 Crime4 days ago
Crime4 days ago
 Education6 days ago
Education6 days ago
 Crime1 week ago
Crime1 week ago

