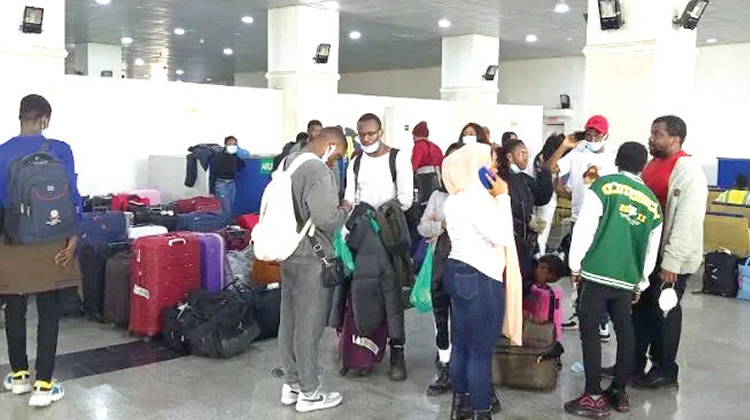
Nigerians spent a sum of $185 million on foreign (medical) health services in the first half of 2022, falling by 65% compared to $528 million recorded in the corresponding period of 2021.
This is according to data included in the country’s balance of payment breakdown, obtained from the Central Bank of Nigeria.
The balance of payment (BOP) breaks down the total amount of forex inflows and outflows in a country wherein a positive balance indicates a current account surplus and a negative current account deficit.
While the amount dropped compared to the corresponding period of 2021, it however increased by 113.1% compared to N86.9 million that was spent in the second half of last year.
Nigerians’ spending on foreign medical services dropped significantly in 2020 in the heat of the pandemic, with travel restrictions being placed and the growing incidence of the disease in other developed countries.
In 2020, Nigerians parted with a sum of $1 billion for foreign health-related expenses, from $2.6 billion recorded in 2019.
It fell further to $615 million in 2021 and could reduce further in 2022. Meanwhile, Nigerians have had a knack for traveling abroad for medical services because of a lack of trust and the inadequacies in the Nigerian health sector.
READ ALSO: Naira crashes to all-time record low as forex scarcity bites
Traveling outside the country, especially for healthcare-related reasons, has declined due to travel restrictions and access to forex.
Additionally, the rising cost of traveling abroad due to the naira devaluation and the global energy crisis has also discouraged foreign traveling, as the globe continues to grapple with the effect of the Russia-Ukraine war.
Nigeria has also attracted a significant increase in new hospitals as millions of dollars in investments pour into the sector.
It is interesting to note that despite the huge outflow, the country, which is dubbed the giant of Africa and the largest economy on the continent received no FX inflows for the same purpose. An indication of how foreigners perceive the state of the Nigerian health sector.
The Global Health Workforce Alliance of the World Health Organization has highlighted some key factors affecting the Nigerian healthcare service sector, some of which include lack of public and private sector coordination, lack of planning based on staffing projection needs, which leads to an overproduction of some categories of health workers at the expense of others.
The health sector is a critical sector of a country’s Sustainable Development Goals and requires that at least 15% of the annual budget be budgeted to the sector, according to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) benchmark.
Compared to South Africa’s 11.9% allocation, Nigeria’s N1.09 trillion appears to still be low. Similarly, Nigeria’s health sector budget stood at N4,935 in 2023 appropriation on a per capita basis.
 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days ago
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days ago
 Crime5 days ago
Crime5 days ago
 Education7 days ago
Education7 days ago
 Health7 days ago
Health7 days ago
 Comments and Issues6 days ago
Comments and Issues6 days ago
 Football6 days ago
Football6 days ago
 Latest6 days ago
Latest6 days ago

