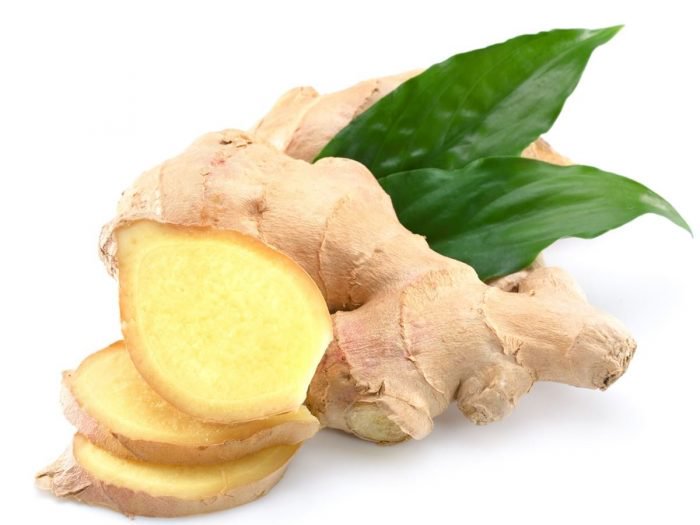
Ginger, also known as Zingiber officinale, is a flowering plant, whose root or rhizome is used as a spice.
It can be consumed in many forms, fresh, dried, powdered, and in the form of oil and juice. Ginger is a common ingredient in Asian cuisines where it is used to build flavors in curries, dressings, and soups.
The top health benefits of ginger include its ability to help with arthritis and osteoarthritis, relieve nausea and pain, prevent cancer, improve respiratory conditions, and reduce flatulence.
Ginger also helps boost bone health, strengthen the immune system, and increase appetite. This spicy root is also good for enhancing sexual activity, mitigating obesity, and relieving the pain related to menstrual disorders.
According to the USDA National Nutrient Database, it is also rich in carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and protein. In terms of minerals, it has sodium, iron, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc. Vitamins in it include vitamin C, folate, vitamin B6, riboflavin, and niacin.
A study published in Nutrition Journal reveals that ginger helps in relieving nausea during pregnancy, but was not as effective in treating problems of vomiting.
Cancer patients who have undergone chemotherapy can benefit from this root as it will relieve the symptoms of nausea and vomiting. Its quick absorption and rapid regulation of body functions cure nausea in people who have undergone surgeries, without any side effects.
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that fresh ginger shows antiviral properties against respiratory tract infections. It can be used in the form of tea for providing relief to sore throat and coughing.
The elevated sugar levels after a meal may cause the stomach to reduce its natural rate of emptying its contents. It helps in regulating high sugar levels and soothing the stomach, thus, maintaining its regular rhythm.
Along with that, it has a number of compounds that improve the absorption of nutrients and minerals from the food we eat. This is why ginger is frequently used as an appetizer or an aperitif since it can stimulate the appetite while preparing the digestive system for an influx of food.
Ginger prevents the occurrence of ulcers, which are generally characterized by bleeding and acute gastric irritability.
People suffering from tuberculosis can benefit from ginger, as it helps prevent hepatotoxicity.
Ginger helps reduce the levels of prostaglandins in the body, hence it aids in relieving cramps. Scientists believe that high levels of prostaglandins contribute to increased menstrual cramps.
Ginger helps regulate the blood sugar levels in people suffering from type 2 diabetes. Glycemic and lipid abnormalities lead to long-term complications in diabetics, as per a research study published in the International Journal of Endocrinology Metabolism in 2017.
Ginger can help in alleviating the symptoms of eczema, owing to its anti-inflammatory properties. By adding ginger tea, or the juice to your diet, you can easily bid goodbye to many chronic skin conditions like dermatitis, acne, and psoriasis.
 Entertainment6 days ago
Entertainment6 days ago
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days ago
 Crime5 days ago
Crime5 days ago
 Education7 days ago
Education7 days ago
 Health7 days ago
Health7 days ago
 Comments and Issues6 days ago
Comments and Issues6 days ago
 Football6 days ago
Football6 days ago
 Latest6 days ago
Latest6 days ago




